ADHD Symptoms
ADHD Symptoms
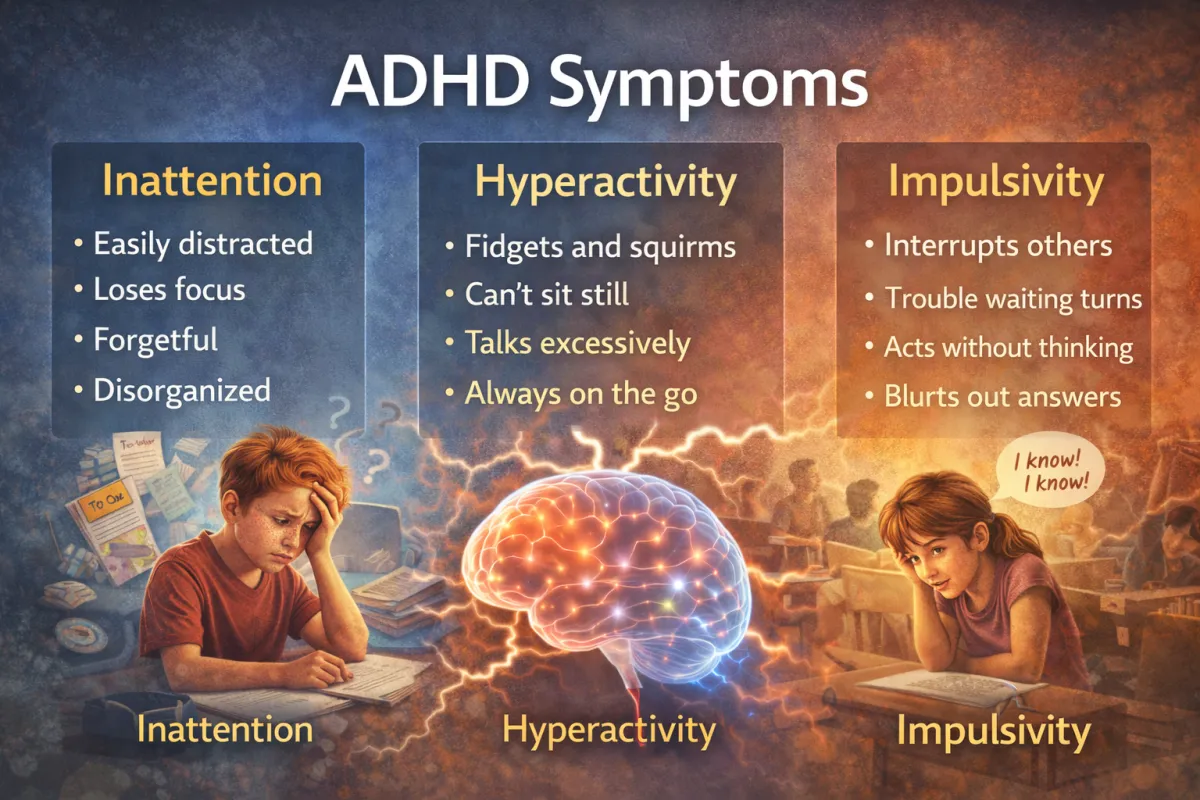
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Symptoms vary by individual and can change with age. A person can be diagnosed with one of three types of ADHD: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, or combined.
Common symptoms of ADHD include:
Inattention:
Difficulty paying attention to details, leading to careless mistakes.
Trouble staying focused on tasks or activities.
Appearing not to listen when spoken to directly.
Struggling to follow through on instructions and finish tasks.
Problems with organization, time management, and meeting deadlines.
Avoiding or disliking tasks that require sustained mental effort.
Losing things frequently (e.g., keys, books, school assignments).
Being easily distracted by unrelated stimuli or thoughts.
Forgetting daily activities, chores, or appointments.
Hyperactivity and Impulsivity:
Fidgeting, tapping hands or feet, or squirming in one's seat.
Having trouble staying seated when it's expected (e.g., in a classroom or at work).
Running, climbing, or being excessively active in inappropriate situations.
Feeling restless or being constantly "on the go."
Talking excessively.
Blurting out answers before a question is finished.
Difficulty waiting for one's turn.
Interrupting or intruding on others' conversations or games.
It's important to note that these symptoms must be persistent, present in two or more settings (e.g., home and school), and significantly interfere with a person's social, academic, or work functioning to be considered for an ADHD diagnosis. Many of these behaviors are common in children, but for those with ADHD, they are severe, continue for at least six months, and are not appropriate for their developmental level.
